INTERNET AND E-MAIL
THE INTERNET
The Internet links private PCs, public networks and business networks together using telephone lines to form one vast world-wide network.
It allows computer users to share and exchange information with each other wherever they are in the world.
The information on the Internet comes in many different formats.
These range from simple e-mail text files to music, video clips, computer software and even live television pictures.
The simplest way to connect to the Internet is to use a dial-up connection.
This type of connection requires a computer with a modem and access to a telephone line.
A modem converts a digital signal into an equivalent analogue signal that can be sent down a telephone line.
At the destination another modem is needed to convert the analogue signal back into a digital signal, which the receiving computer can understand.
The speed of a modem is measured in kilobits per second (Kbps) – this is a measure of how fast data can be transferred.
Dial-up modem connections offer data transfer speeds of up to 52 Kbps.
ISDN digital telephone lines offer a faster connection to the Internet.
ISDN connections offer data transfer speeds of up to 128 Kbps.
Dialup modems and ISDN lines are gradually being replaced by broadband connections that use a system called ADSL.
Broadband connections allow round-the-clock Internet access without having to dial a special telephone number and wait for a connection to be established.
ASDL is much faster than ISDN typically offering data transfer speeds of between 500 Kbps and 1,000 Kbps.
Some larger organisations use a leased line as their method of connection.
This is a private telephone line which is permanently open 24 hours a day.
An Internet Service Provider is a commercial organisation, which provides a connection to the Internet for other businesses or individuals.
Search engines allow users to surf the Internet for information by entering keywords.
Web addresses give the location of individual sites on the World Wide Web.
A web site can be quickly accessed using its address which is often referred to as a URL or Uniform Resource Locator.
A Uniform Resource Locator or URL gives the location of an individual site on the World Wide Web
Most URLs start with http//:www.
URLs often reveal the country of origin such as .uk for the United Kingdom.
URLs also indicate whether a site is commercial with either .co or .com for a commercial organisation, .gov for a government organisation and .ac for academic organisations.
Many businesses now have websites that allow Internet users to buy their goods or services online at any time of day or night throughout the year.
This type of online shopping also offers the advantages of not needing to travel anywhere or get pushed around in crowded shops.
Some companies do all of their business over the Internet and have no ordinary shops.
Advantages of online shopping:
money doesn’t have to be spent on normal business overheads like renting shops and paying employees;
customers can be offered a much wider choice of goods because they can be ordered from suppliers as required rather than having to be kept available on the shelves all the time;
money is not tied up in unsold stock or wasted on products that aren’t popular;
data about customers and their buying habits can be collected directly and used to offer a much more personalised service tailored to suit the needs of an individual customer.
Disadvantages of online shopping:
debit or credit card numbers can be intercepted by hackers during transmission and used to make unauthorised purchases;
criminals can set up fake web sites offering goods or services often using the name of a genuine company;
it is much easier for a business to gather information about its rivals by simply accessing their web sites — this can make it much harder to remain competitive.
Online booking systems allow Internet users to check the availability of and book things like:
theatre, cinema and concert tickets; seats on coaches, trains and aeroplanes; hotel rooms.
An online booking system is essentially a web site that can be used to access a remote database.
Dangers of the Internet:
hackers;
viruses;
undesirable material.
Hackers can be stopped using firewall software.
Viruses are often spread via e-mail and can be removed using virus checking programs.
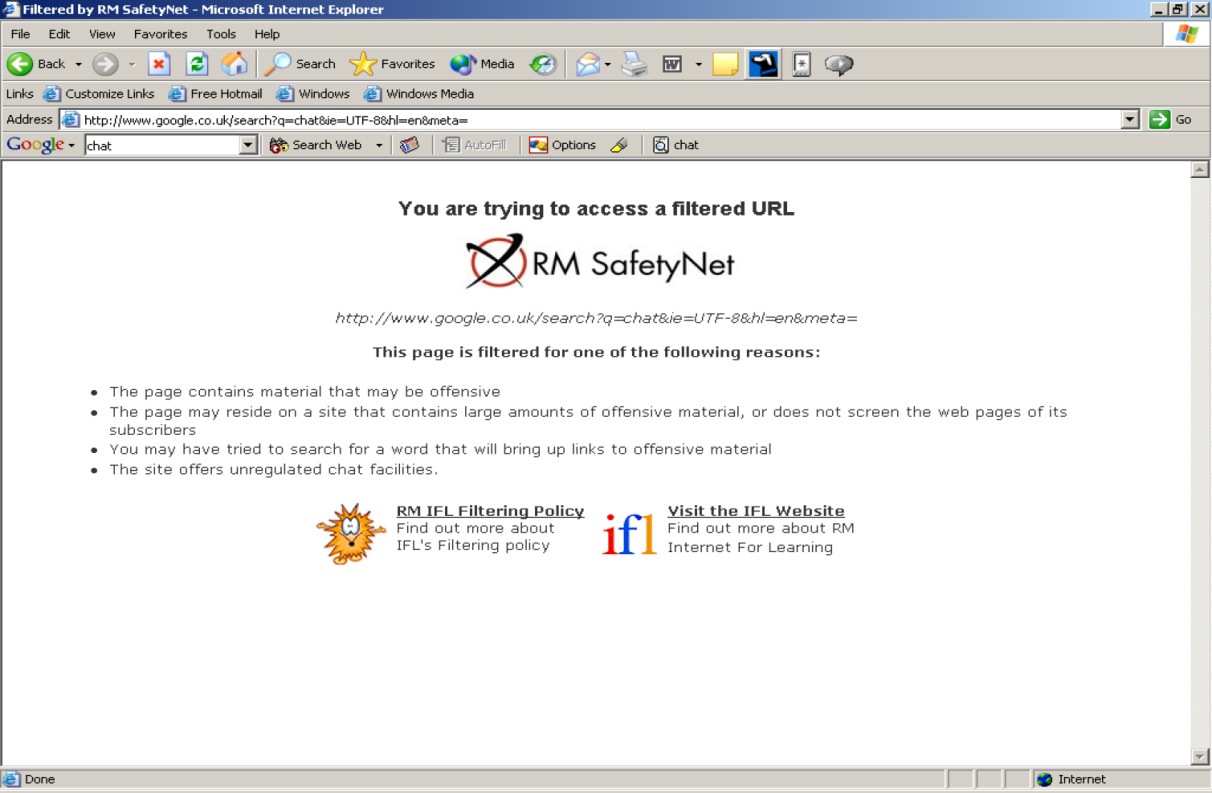
Undesirable material can be blocked using special filtering software and adult supervision.
Advantages of the Internet:
- easy communication with other people around the world;
- valuable learning resource because Internet skills will be needed for jobs in the future;
- enables more people to work from home;
- a vast amount of information can be accessed;
- up-to-date information can be accessed on-line without the need to await publication;
- publishing documents on the Internet saves paper;
- a valuable resource for companies to advertise and conduct business.
Disadvantages of the Internet:
- much of the information isn’t checked and may be incorrect or irrelevant;
- a large amount of undesirable material, such as pornography, is readily available;
- messages sent across the Internet can be easily intercepted and are open to abuse by others;
- large telephone bills can easily be run up;
- too much time spent on the Internet could result in a lack of face-to-face interaction with others and a loss of social skills;
- going on-line runs the risk of hackers or viruses being able to damage your computer.
Comments